What is Lymphedema?
Lymphedema is a swelling caused by damage to the lymphatic system. It usually affects the arms or legs. It may also affect the hands, feet, face, neck, back, chest or genitals.
Signs of lymphedema include swelling of the limbs, and sometimes other areas of the body. Also, the patient will often experience painful burning and aching sensations. These symptoms are often accompanied by fatigue, fibrotic hardening of the skin, and impaired joint mobility.
There are two types of lymphedema: Primary and Secondary.
PRIMARY LYMPHEDEMA –
is the result of an abnormality of the lymphatic system. In most cases it is caused by:
- Congenital Lymphedema (Milroy’s disease) develops in infancy and causes lymph nodes to form abnormally.
- Lymphedema Praecox (Meige’s disease) develops around puberty or during pregnancy, it could occur later, up to age thirty five.
- Lymphedema Tarda (Late-onset lymphedema) rarely develops, but occurs after age thirty five.
SECONDARY LYMPHEDEMA –
is a result of damage to the lymphatic system. Most common causes are due to surgery, mastectomies, radiation, removal of lymph nodes, trauma, and chronic venous insufficiency. It can develop soon after surgery, years later, or not at all. Swelling and inflammation take place when the amount of lymphatic fluid within a given area exceeds the capacity of the lymph vessels to transport it. The lymph fluid then leaks out and accumulates in the fatty tissues under your skin. This excess fluid is moved out of the tissues and back into the bloodstream through the lymph system by muscle contraction, deep breathing (diaphragm muscle contracts when you breathe), stretching of the skin, and by external pressure (compression bandages or garments).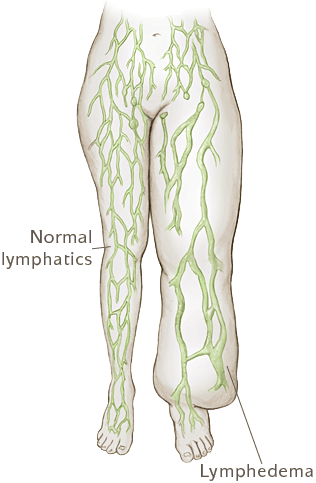
![Compass Therapeutic - White BG Logo Converted [web only]](https://www.compasstherapeutic.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/Compass-Therapeutic-White-BG-Logo-Converted-web-only-scaled.jpg)